
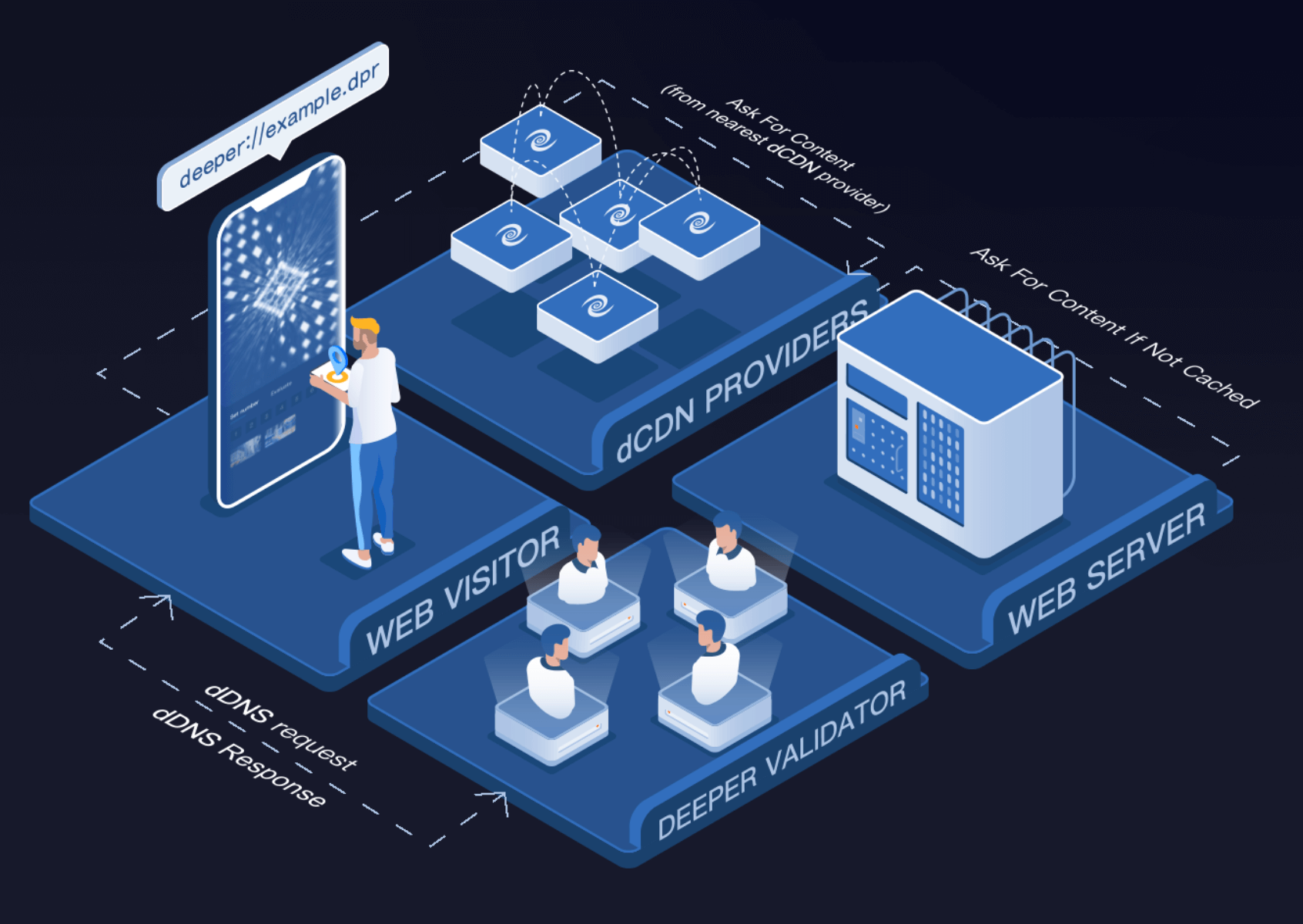
Their technology combines blockchain, network security, and peer to peer network sharing to usher in a decentralized, private, secure, and fair Web 3.0. This will all be made possible with the help of Deeper Network technology and the infrastructure they are building for Web 3.0.ĭeeper Network, an official member of the Substrate Builders Program, is based out of Silicon Valley, Santa Clara, CA. Censorship, cybercrime, and bandwidth costs will be greatly reduced. Almost every aspect of our lives and our continued reliance on large centralized platforms will be done away with. Web 3.0 will eventually mature into a more intuitive, completely decentralized network, with the promise of true sovereignty and freedom for its users. NFTs are another popular blockchain application that has massive implications for the future of social media, art, sports, and entertainment because everyone will have the ability to own and control their own data, as well as creative projects. In fact, we have already begun to see a shift in the way people are using blockchain technology in their daily lives.ĭefi (Decentralized Finance) has given people the ability to do most of the things that centralized banks support - earn interest, borrow, lend, trade assets, and more. The coming version of the internet, Web 3.0, however, aims to address many of these problems with the help of blockchain technology. Instead, we willingly sacrifice our personal data and privacy rights to gain access to the apps we love because we have no choice. Have you ever refused to accept the terms and conditions for apps you use? Probably not. The user has no control over this process. They control who can access their platform, when they can access it, and if they want to, they can restrict access completely. This is because platforms we use, like Twitter and Facebook, are centrally deployed and centrally managed by those companies. Countries can ban websites and censor others. Restrictive ISPs and big tech companies blur the line between internet pioneers and greedy overlords willing to sell our data for ad revenue. Cybercrime, censorship, surveillance, and expensive bandwidth costs are big problems. However, despite all these advancements, Web 2.0 still has its challenges. And Bitcoin, the first real world application of blockchain technology, was launched. Airbnb, Uber, and Lyft gave rise to the global sharing economy. Reddit is a trusted news source for billions of people worldwide. E-Bay created instant marketplaces and made buying and selling easy. Ecommerce and online banking became the norm. Enhancements to technologies like Javascript, HTML5, and CSS3 enabled startups to build the interactive platforms that have come to define the internet like YouTube, Twitter, and Facebook.

It is more accessible for billions of people and allows us to share information on a global scale. The current version of the internet, Web 2.0, is referred to as the Social Web. The internet was a one way street populated with content created from a small group of individuals and companies. Commenting on articles, creating user profiles, and algorithms to sift through web pages were virtually nonexistent. However, it was not very sophisticated and the network infrastructure was not fully developed. Web 1.0, known as the Static Web, was the first reliable version of the internet. This new iteration of the internet is called Web 3.0. The internet as we know it is rapidly evolving and will change everything about how we interact with the world.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
